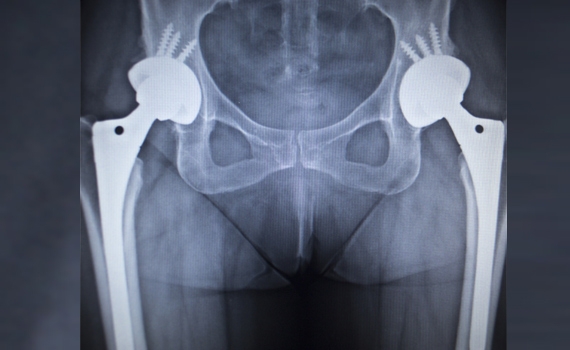
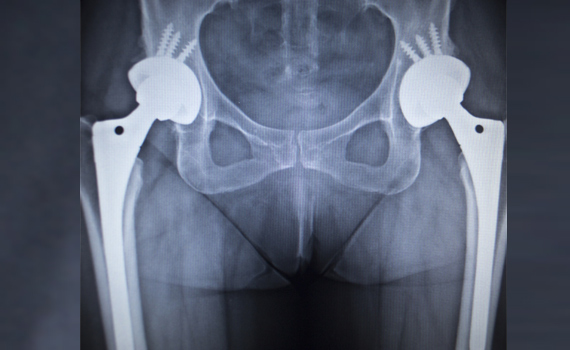
A hip replacement is a surgical procedure that involves removing a damaged or worn hip joint and replacing it with an artificial joint. People over the age of 60 are more likely to need a hip replacement, however this can be required at any age.
A hip replacement is usually offered to people that are suffering from significant hip pain and have failed to have to have successful pain management from more conservative methods of treatment. Modern technologies mean that hip replacements can now last around 15 years before they need replacing.
Osteoarthritis, a form of arthritis, is the most common reason for hip replacements. Other conditions that may require a hip replacement include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Fractured hip
- Unusual bone growth
Like many other surgeries, a hip replacement may only be recommended if conversative methods of treatment, such as physical therapy, or pain medications, have been unsuccessful.
A hip replacement can either be done under general anaesthetic, meaning that you will be asleep during the procedure; or under spinal anaesthetic, in which you will be awake, however you will not feel anything from the waist down. This surgery will generally take a few hours.
Most people will stay in hospital for 2-3 nights after a hip replacement to ensure that there are no complications. Your doctor will give you instructions to follow when returning home that will help to aid a fast recovery.
People that have a hip replacement are at a higher risk of developing a blood clot. During and after the surgery you will be given stockings that will help to reduce the risk of blood clot forming in the legs. You will also be encouraged to make small movements after the surgery to help prevent this.
After around 6-12 weeks people should notice a significant reduction in the pain that they were experiencing and start to become more active. People should expect to see continued improvement and return to normal everyday activities 6-8 months after the surgery.
This article is intended to inform and give insight but not treat, diagnose or replace the advice of a doctor. Always seek medical advice with any questions regarding a medical condition.